OSPF (Open Shortest Path First)
Network Theory
224.0.0.5, ABR, ASBR, ATM, BDR, DBD, DR, Frame Relay, Link State, Loopback Interface, LSA, LSA Flooding, LSAck, LSR, LSU, NBMA, NSSA, O E1, O E2, O IA, OSPF, OSPF Cost, Router-ID, Stub, Totally Stub, X.25
1 Comment
Bagian dari Dynamic Protocol yang merupakan Link-State…OSPF akan kita kupas tuntas
Secara tajam…setajam…..SILET
*CUTTTT !!!!….kebanyakan infotaintment luh jadi alay !!

Untuk langsung konfigurasi bisa lihat disini (spoiler alert…belum gw “perbaharui” itu artikel)
OSPF dikembangkan oleh IETF, but… at the same time, ISO was working on a link-state routing protocol of their own, Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS). Not surprisingly, IETF chose OSPF as their recommended IGP (Interior Gateway Protocol)
-.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.-
LSP dari OSPF
OSPF packet itu ada 5 tipe

Liat cara kerja Link-State
-.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.-
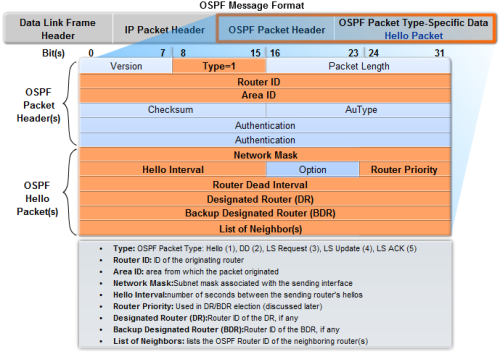
Hello Packet
Hello packets are used to:
Yang penting2 apa aja sih??:

Hello packet ini juga mengirimkan OSPF router ID, buat apa sih ?? sebagai “nama” dari router yang menjalankan OSPF
Contoh: interface fa0/0 di router Cisco 1841 dikasih ip 10.1.1.1 dan di fa0/1 dikasi 172.16.1.1 , maka yang menjadi ID si router OSPF ini adalah 172.16.1.1 (nama si router nya bukan paijo, tukimin, dan lain-lain haha…namanya pake IP)…dan ya, IP yang paling tinggi yang jadi router ID (klo kita ga set manual yah..)

*loopback interface adalah interface “bayangan”, klo interface FastEthernet dan serial secara fisik bisa dilihat…loopback tidak, purpose nya bisa untuk router ID di OSPF atau untuk simulasi network
-.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.-
LSU (Link State Update)
Dalam LSU terdapat 1 atau lebih LSA (Link State Advertisement), jadinya kadang2 LSA bisa di sebut LSU
LSA sendiri adalah BROADCAST packet (ya..broadcast) yang isi paket nya terdiri dari informasi2 yang dibutuhkan oleh router seperti neighbor information dan path cost
LSA inilah yang meng-influence routing table di OSPF

Header Packet dari LSA itu 20 byte. didalam LSA Header itu terdapat link-state ID

-.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.-
Cisco OSPF Metric
Seperti yang kita ketahui…RIP memakai Hop untuk metric dan EIGRP memakai bandwidth dan delay (walaupun ada 2 lagi)
OSPF ini memakai cost, yang mana cost ini adalah Bandwidth-bandwidth juga ujung2nya…haha


-.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.-
OSPF in multi-access network

OSPF defines five network types:
Masalah dalam OSPF di multi akss adalah Flooding LSA (liat point diatas)


Figure 1. LSA Flooding
Masalah OSPF di multi akses network di ibaratkan seperti ini:
Gw berada di suatu ruangan yang penuh dengan orang, bagaimana jadinya jika gw harus introduce diri gue ke semua orang itu, dan masing2 orang lain juga harus mengenalkan diri ke yang lain pula
Udah gitu pas gw udah kenal dengan satu orang, gw harus kenalan lagi dengan yang lain dan GW HARUS NGASIH TAU NAMA YANG UDA GW KENAL KE ORANG YANG LAIN LAGI!!!
Mateee…

Liat cara kerja Link-State (Kalau bingung)
-.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.-
Solusi untuk OSPF Multi-Akses
Yaitu dengan meng-elect (menunjuk) satu router untuk jadi “leader” yang mengirimkan LSA, yang dinamakan DR (Designated Router) dan “cadangan”nya kalau2 DR nya mati…yang disebut Backup Designated Router (BDR)
Klo dipikir2…mirip kek fitur switch yang disebut VTP…Cuma switch server yang boleh kasih info VLAN ke switch yang lain


-.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.-
DR BDR Election Process
Router ID (entah Router-ID, IP interface, atau IP Loopback) yang paling tinggi akan menjadi DR

The election process only takes a few seconds. If all of the routers on the multiaccess network have not finished booting, it is possible that a router with a lower router ID will become the DR. This could be a lower-end router that took less time to boot. (bisa jadi klo router yang ID nya paling tinggi itu LAMA bootingnya…dia ga jadi DR)
Contoh dari gambar diatas…Router C lelet, yang jadi DR adalah Router B…Router C selesai booting…Router B TETEP JADI DR dan Router A jadi BDR
Kalau Router B mati, akan digantikan oleh Router A…nah untuk “suksesor” WAKIL PRESIDEN nya kosong
wakil presidennya uda jadi presiden…presidennya mangkat kek Bapak Soeharto digantikan oleh Bapak Habibie
disinilah router A akan jadi BDR
pertanyaannya bisa ga di rubah “prioritas”nya ??? bisa…ada commandnya koq
bahkan kita bisa modifikasi timer nya (liat paling atas)
-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-
Tipe Route OSPF
klo RIP diwakili dengan huruf R di routing table dan EIGRP dengan D (DUAL), maka di OSPF terdapat 4 type of route
E1 – biasanya digunakan untuk menghubungkan rute2 dari berbagai macam routing protocol didalam satu ISP, metricnya akan bertambah sendiri tergantung dari berapa besar cost (bandwidth) yang dilalui tiap titik.
E2 (Default) – bedanya dengan E1 adalam metricnya tetap…klo E2 metricnya 1120…di SEMUA router ospf akan bilang metricnya 1120…tapi klo E1 akan dikalkulasi lagi, tergantung dari berapa banyak link yang dilewati
ABR = Router yang menghubungkan beda area
ASBR = Router yang menghubungkan OSPF dengan Routing protocol lain
-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-
Tipe Area dalam OSPF
1. Standard Area – yang biasa (kirim summary, link update, dan external route)
2. Backbone Area – atau yang biasa disebut Area 0, semua area yang terhubung ke Area 0 akan bisa ping2an, Backbone juga salah satu standard area
3. Stub Area – ga nerima external route. Klo mo kirim ke luar, router cuma kirim lewat default route (0.0.0.0). Stub area ga bisa punya ABR (ya eyaa laaa)
4. Totally Stubby Area – ga nerima summary route dan external route (klo stub masi nerima summary route), tipe Area ini cuma Cisco Propiertary
5. Not-So-Stubby-Area (NSSA) – sama kek stub2 yang lain, cuma dia boleh punya ASBR dan bisa nerima internal dan external (cuma memang ga diterusin ke external networknya)…pake LSA tipe 7
NSSA ini ibarat klo di view jaringan kita itu STUB…cuma dibalik stub itu ada routing protocol lain yang punya beberapa network (router kita ternyata ASBR)
6. Totally Stubby NSSA – apaan lagi nihhh??? sama kek NSSA, cuma hanya default route aja


next….insya Alloh EIGRP teorinya kita bahas…
Secara tajam…setajam…..SILET
*CUTTTT !!!!….kebanyakan infotaintment luh jadi alay !!

Untuk langsung konfigurasi bisa lihat disini (spoiler alert…belum gw “perbaharui” itu artikel)
OSPF dikembangkan oleh IETF, but… at the same time, ISO was working on a link-state routing protocol of their own, Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS). Not surprisingly, IETF chose OSPF as their recommended IGP (Interior Gateway Protocol)
-.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.-
LSP dari OSPF
OSPF packet itu ada 5 tipe

- Hello, tidak perlu dijelaskan
- DBD, ini penyakit yang disebarkan oleh nyamuk *ehem* DBD packet berisi list versi singkat dari sending router link-state database dan digunakan oleh receiving router untuk meng-compare dengan miliknya.
- LSR, receiving router bisa meminta (request) more information di DBD yang diterima
- LSU, ini packet untuk merespon LSR dan juga untuk announce new information. LSU contain 7 Link-State Advertisement (LSA)
- LSAck, ini paket ketika LSU diterima oleh receiving router
Liat cara kerja Link-State
-.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.-
Hello Packet
Hello packets are used to:
- Discover OSPF neighbors and establish neighbor adjacencies.
- Advertise parameters on which two routers must agree to become neighbors.
- Elect the Designated Router (DR) and Backup Designated Router (BDR) on multiaccess networks like Ethernet and Frame Relay.

Yang penting2 apa aja sih??:
- Type: OSPF Packet Type =Hello (1), DBD (2), LS Request (3), LS Update (4), LS ACK (5)
- Router ID: IP dari router yang ngirim paket
- Area ID: area/wilayah darimana paket itu berasal
- Network Mask: Subnet mask associated with the sending interface
- Hello Interval: number of seconds between the sending router’s hellos
- Router Priority: Used in DR/BDR election (nanti dibawah dijelasin)
- Designated Router (DR): Router ID of the DR, if any
- Backup Designated Router (BDR): Router ID of the BDR, if any
- List of Neighbors: lists the OSPF Router ID of the neighboring router(s)
- Hello Interval (default): 10 second on multi-access and 30 on *non-broadcast multi access (NBMA) such as Frame Relay, X.25, ATM
- OSPF Hello packets are sent as multicast to an address reserved (224.0.0.5)
- Using a multicast address allows a device untuk meng-ignore packet jika sebuah interface tidak OSPF Enabled. Jadi ga perlu repot2 proses paket (saves CPU processing time on non-OSPF devices).
- Dead Interval is the period (dalam detik) that the router will wait to receive a Hello packet from neighbor before declaring that neighbor “down.”
- Dead Interval for Multi access is 40 second and NBMA is 120 second
- Network Type…
- Hello packet juga menentukan DR (Designated Route) dan BDR (Backup DR) guna menghemat/memangkas traffic yang ada di MULTIAKSES NETWORK (klo bukan multi akses…ga perlu DR & BDR)

Hello packet ini juga mengirimkan OSPF router ID, buat apa sih ?? sebagai “nama” dari router yang menjalankan OSPF
Contoh: interface fa0/0 di router Cisco 1841 dikasih ip 10.1.1.1 dan di fa0/1 dikasi 172.16.1.1 , maka yang menjadi ID si router OSPF ini adalah 172.16.1.1 (nama si router nya bukan paijo, tukimin, dan lain-lain haha…namanya pake IP)…dan ya, IP yang paling tinggi yang jadi router ID (klo kita ga set manual yah..)

*loopback interface adalah interface “bayangan”, klo interface FastEthernet dan serial secara fisik bisa dilihat…loopback tidak, purpose nya bisa untuk router ID di OSPF atau untuk simulasi network
-.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.-
LSU (Link State Update)
Dalam LSU terdapat 1 atau lebih LSA (Link State Advertisement), jadinya kadang2 LSA bisa di sebut LSU
LSA sendiri adalah BROADCAST packet (ya..broadcast) yang isi paket nya terdiri dari informasi2 yang dibutuhkan oleh router seperti neighbor information dan path cost
LSA inilah yang meng-influence routing table di OSPF

Header Packet dari LSA itu 20 byte. didalam LSA Header itu terdapat link-state ID

-.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.-
Cisco OSPF Metric
Seperti yang kita ketahui…RIP memakai Hop untuk metric dan EIGRP memakai bandwidth dan delay (walaupun ada 2 lagi)
OSPF ini memakai cost, yang mana cost ini adalah Bandwidth-bandwidth juga ujung2nya…haha


-.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.-
OSPF in multi-access network

OSPF defines five network types:
- Point-to-point
- Broadcast Multiaccess
- Nonbroadcast Multiaccess (NBMA)
- Point-to-multipoint
- Virtual links
Masalah dalam OSPF di multi akss adalah Flooding LSA (liat point diatas)


Figure 1. LSA Flooding
Masalah OSPF di multi akses network di ibaratkan seperti ini:
Gw berada di suatu ruangan yang penuh dengan orang, bagaimana jadinya jika gw harus introduce diri gue ke semua orang itu, dan masing2 orang lain juga harus mengenalkan diri ke yang lain pula
Udah gitu pas gw udah kenal dengan satu orang, gw harus kenalan lagi dengan yang lain dan GW HARUS NGASIH TAU NAMA YANG UDA GW KENAL KE ORANG YANG LAIN LAGI!!!
Mateee…

Liat cara kerja Link-State (Kalau bingung)
-.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.-
Solusi untuk OSPF Multi-Akses
Yaitu dengan meng-elect (menunjuk) satu router untuk jadi “leader” yang mengirimkan LSA, yang dinamakan DR (Designated Router) dan “cadangan”nya kalau2 DR nya mati…yang disebut Backup Designated Router (BDR)
Klo dipikir2…mirip kek fitur switch yang disebut VTP…Cuma switch server yang boleh kasih info VLAN ke switch yang lain


-.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.–.-.-.-
DR BDR Election Process
Router ID (entah Router-ID, IP interface, atau IP Loopback) yang paling tinggi akan menjadi DR

The election process only takes a few seconds. If all of the routers on the multiaccess network have not finished booting, it is possible that a router with a lower router ID will become the DR. This could be a lower-end router that took less time to boot. (bisa jadi klo router yang ID nya paling tinggi itu LAMA bootingnya…dia ga jadi DR)
Contoh dari gambar diatas…Router C lelet, yang jadi DR adalah Router B…Router C selesai booting…Router B TETEP JADI DR dan Router A jadi BDR
Kalau Router B mati, akan digantikan oleh Router A…nah untuk “suksesor” WAKIL PRESIDEN nya kosong
wakil presidennya uda jadi presiden…presidennya mangkat kek Bapak Soeharto digantikan oleh Bapak Habibie
disinilah router A akan jadi BDR
pertanyaannya bisa ga di rubah “prioritas”nya ??? bisa…ada commandnya koq
bahkan kita bisa modifikasi timer nya (liat paling atas)
-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-
Tipe Route OSPF
klo RIP diwakili dengan huruf R di routing table dan EIGRP dengan D (DUAL), maka di OSPF terdapat 4 type of route
- O – Rute OSPF biasa (intra area)
- O IA – Rute OSPF yang didapat dari OSPF area lain
- O E1 – Rute OSPF yang didapat dari different routing protocol
- O E2 - Rute OSPF yang didapat dari different routing protocol
E1 – biasanya digunakan untuk menghubungkan rute2 dari berbagai macam routing protocol didalam satu ISP, metricnya akan bertambah sendiri tergantung dari berapa besar cost (bandwidth) yang dilalui tiap titik.
E2 (Default) – bedanya dengan E1 adalam metricnya tetap…klo E2 metricnya 1120…di SEMUA router ospf akan bilang metricnya 1120…tapi klo E1 akan dikalkulasi lagi, tergantung dari berapa banyak link yang dilewati
ABR = Router yang menghubungkan beda area
ASBR = Router yang menghubungkan OSPF dengan Routing protocol lain
-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-.-
Tipe Area dalam OSPF
1. Standard Area – yang biasa (kirim summary, link update, dan external route)
2. Backbone Area – atau yang biasa disebut Area 0, semua area yang terhubung ke Area 0 akan bisa ping2an, Backbone juga salah satu standard area
3. Stub Area – ga nerima external route. Klo mo kirim ke luar, router cuma kirim lewat default route (0.0.0.0). Stub area ga bisa punya ABR (ya eyaa laaa)
4. Totally Stubby Area – ga nerima summary route dan external route (klo stub masi nerima summary route), tipe Area ini cuma Cisco Propiertary
5. Not-So-Stubby-Area (NSSA) – sama kek stub2 yang lain, cuma dia boleh punya ASBR dan bisa nerima internal dan external (cuma memang ga diterusin ke external networknya)…pake LSA tipe 7
NSSA ini ibarat klo di view jaringan kita itu STUB…cuma dibalik stub itu ada routing protocol lain yang punya beberapa network (router kita ternyata ASBR)
6. Totally Stubby NSSA – apaan lagi nihhh??? sama kek NSSA, cuma hanya default route aja


next….insya Alloh EIGRP teorinya kita bahas…
Network Basic Theory 10 (WAN Technology Concept)
April 2, 2012
Network Theory
ADSL, ATM, B Channel, BRI channel, Cable Modem, Cell Switched, Circuit Switched, CO, CPE, CSU/DSU, D Channel, DCE, Demarcation Point, DLCI, DSL, DSLAM, DTE, Ethernet, Fiber Optic, Frame Relay, HDLC, ISDN, Leased Line, Local Loop, MetroEthernet, MPLS, Packet Switched, PPP, PRI Channel, PSTN, T1, VPN, wi-fi, WiMax, X.25
Leave a comment

Figure 1. WAN berada di layer 1 & 2

Gw akan jelaskan gambar diatas
Yang bagian kanan adalah ISP Equipment (gw bacanya si…alat2 di HQ / HeadQuarter)
- Central Office (CO): A local service provider facility or building where local telephone cables link to long-haul, all-digital, fiber-optic (tempat backbone)
- Local Loop: A local service provider facility or building where local telephone cables link to long-haul, all-digital, fiber-optic (lo bisa baca…kabel dari ISP ke tempat subscriber/konsumen)
- Demarcation Point: nah…kabel dari ISP kecolok di demarcation point ini…disini tempat alat2 consumen untuk konek ke ISP, taken from Cisco CNAP “demarcation point is A point established in a building or complex to separate customer equipment from service provider equipment. Physically, the demarcation point is the cabling junction box, located on the customer premises, that connects the CPE wiring to the local loop. It is usually placed for easy access by a technician. The demarcation point is the place where the responsibility for the connection changes from the user to the service provider. This is very important because when problems arise, it is necessary to determine whether the user or the service provider is responsible for troubleshooting or repair.” Di demarcation point inilah biasanya ISP Technical Support atau Help Desk bisa bantu
Customer “Alo….inet gw putus nih“
Call Support “[segala persyaratan ditanyain]…ok..saya cek yah koneksi ke tempat bapak…“
(saat cek koneksi…mereka cek…bisa ga nge-ping dari kantor pusat ke demarcation point…bukan ke computer lo ya…)
(kalau nyambung) Call Support “map bapak…di kami sepertinya tidak ada masalah“
Biasanya akan diikuti oleh kata2 seperti ini, Customer “eh njing…inet gw mati…ga ada masalah gimana!?!?!” wkwkwkwk
(nah..klo nyambung…berarti dari local loop/kantor pusat ke demarcation point ga ada masalah….masalahnya ada di demarcation point ke modem lo)
Call Support “baik pak…technical support kami akan membantu bapak dalam 3×24 jam…blablabla“
Nah..itu kan kalo nyambung….klo putus??berarti dari ISP nya bermasalah…
Paling Call Support nya bilang gini “baik pak, ada SEDIKIT GANGGUAN TEKNIS dalam jaringan kami…mohon menunggu sebentar”
Yang bagian kiri dari gambar diatas adalah Customer Premises Equipment (CPE): yaitu alat2 dan wiring(kabel2) yang berlokasi di Subscriber/Konsumen, bisa aja alat nya dari ISP atau mereka beli (atau sewa)
- Data Communication Equipment: Also called data circuit-terminating equipment, the DCE consists of devices that put data on the local loop. The DCE primarily provides an interface to connect subscribers to a communication link on the WAN cloud…yaitu alat2 untuk berhubungan dengan ISP (demarcation point)
- Data Terminal Equipment: The customer devices that pass the data from a customer network or host computer for transmission over the WAN. The DTE connects to the local loop through the DCE…klo di kita bisa saja ini dikatakan modem

-
ModemPerlu dijelasin ?? ga usa kali ye..gampang ini ma
-
Router’nuff said too
-
Core CouterBedanya ama router biasa adalah router ini adanya di backbone…
-
Access ServerConcentrates dial-in and dial-out user communications. An access server may have a mixture of analog and digital interfaces and support hundreds of simultaneous users
-
WAN SwitchSwitch di Backbone…biasanya ngalirin data2 Frame Relay dan bahkan PSTN Switch (Telepon)
-
CSU/DSUDigital lines, such as T1 or T3 carrier lines (bedanya Cuma dikecepatan doank, T1 = 1,5 Mbps dan T3 = 44 Mbps), require a channel service unit (CSU) and a data service unit (DSU). The two are often combined into a single piece of equipment, called the CSU/DSU. The CSU provides termination for the digital signal and ensures connection integrity through error correction and line monitoring. The DSU converts the T-carrier line frames into frames that the LAN can interpret and vice versa….koq kek modem ya ??emang !!!.The CSU/DSU implements two different functions. The CSU is responsible for the connection to the telecom network while the DSU is responsible for handling the interface with the DTE. Bedanya ama modem2 kebanyakan adalah CSU/DSU mengirim data dalam format digital melalui jaringan telephone digital.

Ada 1 lagi…Multi Protocol Label Switching (MPLS)..tapi dibahasnya di CCNP…kita ga bahas MPLS dulu nanti deh ya (MPLS ada bab sendiri hehe)


Gambar diatas adalah diagram frame dari HDLC (salah satu dari WAN Protocol). Examining the header portion of an HDLC frame will help identify common fields used by many WAN encapsulation protocols. The frame always starts and ends with an 8-bit flag field. The bit pattern is 01111110. The address field is not needed for WAN links, which are almost always point-to-point. The address field is still present and may be 1 or 2 bytes long. The control field is protocol dependent, but usually indicates whether the content of the data is control information or network layer data. The control field is normally 1 byte.
Together the address and control fields are called the frame header. The encapsulated data follows the control field. Then a frame check sequence (FCS) uses the cyclic redundancy check (CRC) mechanism to establish a 2 or 4 byte field.

Woke…sekarang kita bahas Opsi2 koneksi dari WAN
Ada 4…Leased Line, Circuit-switched, Packet-switched, dan Broadband
-
Leased Line: tipe koneksi WAN secara private yang dedicated…alias lo bener2 nyewa dari ISP…anggeplah 1Mbps…ya 1 Mbps…1 banding 1 (1:1)…ga di share ama yang lain

Apa aja yang dibutuhkan untuk Leased Line…
- CSU/DSU Device
- Serial Cable

*56 & 64 berarti kecepatan
*Huruf T berarti kabel2 standar dari
Amerika Utara, Jepang, dan Korea Selatan, Huruf E berarti standar Eropa
(beda cara multiplexing nya doank…cara ngalirin listriknya)
*OC means Optical Cable…Fiber Optic let’s say
*J ??ga tau gw…hahahahhah
-
Circuit-Switched: contohnya adalah PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network…lo bisa bilang ini jaringan telepon lah) dan ISDN (Integrated Service Digital Network…versi digitalisasi PSTN).

Contoh diatas adalah bagaimana telepon “mengakses” telepon lainnya…dengan cara meng-establish circuit (membangun sirkuit/jembatan antar A dan B…makanya dinamakan circuit switching), jika teleponnya diganti dengan modem…maka computer data bisa di alirkan lewat jaringan telepon ini (contoh: telkomnet instan). Jeleknya circuit switching adalah…salah satu dari circuit yang dilalui data suara putus…putus sudah semua conversation dari telepon A ke telepon B
-
ISDN: is a circuit-switching technology that enables the local loop of a PSTN to carry digital signals, resulting in higher capacity switched connections. ISDN changes the internal connections of the PSTN from carrying analog signals to time-division multiplexed (TDM) digital signals. TDM allows two or more signals or bit streams to be transferred as subchannels in one communication channel. The signals appear to transfer simultaneously, but physically are taking turns on the channel. A data block of subchannel 1 is transmitted during timeslot 1, subchannel 2 during timeslot 2, and so on. One TDM frame consists of one timeslot per subchannel. Salah satu protocol yang memakai TDM adalah PPP. ISDN connection uses 64 kb/s bearer channels (B) for carrying voice or data and a signaling, delta channel (D) for call setup and other purposes.

-
There are 2 types of ISDN interface:
-
BRI Channel: Basic Rate Interface…untuk koneksi rumahan, terdiri dari 2 kabel B dan 1 kabel D (64 kb/s untuk B channel dan 16 kb/s untuk D channel)

Nah…di BRI Channel Interface…yang D Channel jarang di gunain…jadi kadang2 provider internet make itu channel buat carry data, yang sekarang dikenal namanya X.25 (9,6 kb/s) -
PRI Channel: Primary Rate Interface…23 kabel untuk B channel dan 1 kabel untuk D channel yang ditotal2 jadi 1,544 Mbps, yang kita kenal dengan T1 (North America). Untuk eropa, Australia, dan beberapa Negara yang lain..pake nya 30 kabel untuk B channel

-
-
-
Packet-Switched: data yang dialirkan dari A ke B dipecah2 jadi packet (makanya dinamakan packet switching) lalu dialirkan ke B melalui redundant network…jadi bisa aja suatu data dipecah jadi 3 bagian…bagian A1 lewat jawa, bagian A2 lewat Kalimantan, bagian A3 lewat papua…yang menting nyampe di bali (kira2 analoginya begitu). Path yang diambil tergantung dari switch dan router nya (connection-oriented atau connectionless…inget TCP/UDP !!)…klo di Frame Relay dikenal namanya Data Link Control Indentifier (DLCI…ini istilah TCP untuk Frame Relay).
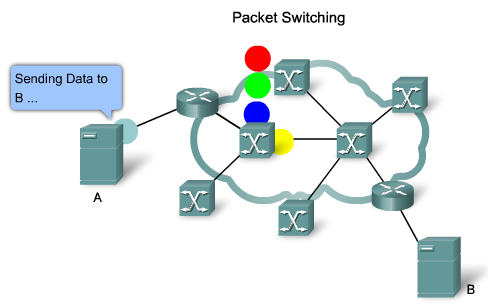
Jeleknya apa dari Packet-Switched ini ?? karena paketnya dipecah2….nyampe nya ga bisa di prediksi…Delay, Jitter, dll dah…
Contohnya Technology nya adalah Frame Relay, X.25, ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Module)…nanti aye jelasin yeee -
Yang Terakhir adalah…INTERNET !!!: contoh technology WAN-nya adalah VPN..yang bisa di create melalui DSL (Digital Subscriber Line….ADSL..ya speedy noh…ada ADSL ada SDSL), Wi-Fi, Cable (Fiber)
- A dari ADSL singkatan dari Asymmetric…sesuai dengan ciri2 DSL pada umumnya…kecepatan upstream dan downstream-nya berbeda…klo ADSL Downstreamnya yang lebih gede
- S dari SDSL adalah Symmetric…opposite dari ADSL…dia upstream nya lebih gede…makanya kurang popular buat dijadiin Internet Service
- Ada lagi yang namanya VDSL…V for Very High Bit Rate…downstream bisa ampe 52Mbit/s dan 12Mbit/s untuk upstream…Cuma implementasinya mahal (enakan ADSL….murah..untungbanyak), buat dijadiin ISP juga ga cocok..mending Fiber Optic sekalian…ya ga ?!?!?
- JADIIIII…..DSL itu make kabel telepon….kabel telepon itu dipake buat suara kan ?!? ternyata kabel itu Cuma 10% doank potensi yang dipake….nah..ini dia yang di “exploitasi” oleh DSL…ngalirin data dari internet TANPA harus ganggu data suara
Ada 3 yang umum dipakai…X.25, Frame Relay (kita bisa bilang ini anak nya X.25), dan ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Module)
- X.25: teknologi X.25 menggunakan Virtual circuits (VC) yang di-established melalui network dengan call request packets ke alamat tujuan. The resulting SVC (Switched VC) is identified by a channel number. Data packets labeled with the channel number are delivered to the corresponding address. Multiple channels can be active on a single connection. Aplikasi nyata dari X.25 ini adalah point-of-sale card readers. These readers use X.25 in dialup mode to validate transactions on a central computer. For these applications, the low bandwidth and high latency are not a concern, and the low cost makes X.25 affordable. X.25 link speeds vary from 2400 b/s up to 2 Mb/s. However, public networks are usually low capacity with speeds rarely exceeding above 64 kb/s. UDAH JARANG DIGUNAIN DI NEGARA2 MAJU DAN BERKEMBANG.
-
Frame Relay: mirip kek X.25 tapi channel number nya diganti dengan Data Link Control Identifier (jadi packet nya di-”tag” dengan DLCI layer 2, bukan dari layer 3 lagi)

Transfer data yang ditawarkan oleh Frame Relay bisa sampai 4 Mb/s. Frame Relay is ideal for connecting enterprise LANs. The router on the LAN needs only a single interface, even when multiple VCs are used (jadi 1 interface bisa banyak DLCI alias banyak tujuan). The short-leased line to the Frame Relay network edge allows cost-effective connections between widely scattered LANs. -
ATM : singkatan dari Asynchronous Transfer Mode, is a technology capable of transferring voice, video, and data through private and public networks. It is built on a cell-based architecture (sama kek Packet Switching,tapi pemecahan packet2 nya fix / fixed length…makanya dinamakan “Cell”) rather than on a frame-based architecture. ATM cells are always a fixed length of 53 bytes (5 byte ATM header dan 48 bytes ATM payload). Small, fixed-length cells are well suited for carrying voice and video traffic because this traffic is intolerant of delay. Video and voice traffic do not have to wait for a larger data packet to be transmitted.
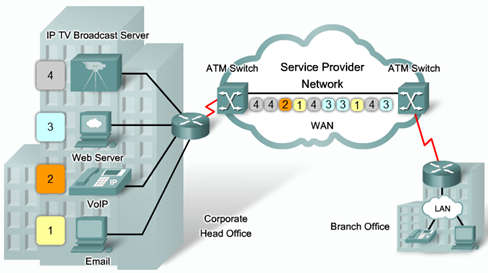
The 53 byte ATM cell is less efficient than the bigger frames and packets of Frame Relay and X.25. When the cell is carrying segmented network layer packets, the overhead is higher because the ATM switch must be able to reassemble the packets at the destination. A typical ATM line needs almost 20 percent greater bandwidth than Frame Relay to carry the same volume of network layer data. ATM was designed to be extremely scalable and can support link speeds of T1/E1 to OC-12 (622 Mb/s) and higher.
Nah…kali ini kita akan bahas namanya DSL, Wi-Fi, dan Cable Modem
-
DSL: singkatan dari Digital Subscriber Line, penjelasannya udah diatas tuh. Multiple DSL subscriber lines are multiplexed into a single, high-capacity link using a DSL access multiplexer (DSLAM) at the provider location. DSLAMs incorporate TDM technology to aggregate many subscriber lines into a single medium, generally a T3 (DS3) connection. Current DSL technologies use sophisticated coding and modulation techniques to achieve data rates of up to 8.192 Mb/s.


-
Cable Modem: Technology Cable Modem ini menggunakan Coaxial cable dan widely used in urban areas to distribute television signals. Network access is available from some cable television networks. This allows for greater bandwidth than the conventional telephone local loop (contoh nyata First Media dengan Indovision + FastNet nya). Jadi pengguna TV Kabel bisa akses internet dengan menggunakan kabel TV nya itu (yang dinamakan cable headend). Komponen penting dari headend ini adalah cable modem termination system (CMTS) untuk send dan receive digital cable signal buat internetanTaken from CNAP Exploration 4 (1.3.5.1): “Cable modem subscribers must use the ISP associated with the service provider. All the local subscribers share the same cable bandwidth. As more users join the service, available bandwidth may be below the expected rate“
-
Wi-Fi: singkatan dari Wireless Fidelity, ada 3 tipe Wi-Fi (kata Cisco sih)
- Municipal Wi-Fi: wifi di kantor, di rumah, di gedung2, antar gedung, atau 1 kota
- Satellite Internet: ini dia….yang paling canggih…Internetan pakek satelit wkwkwk. Untuk bisa internetan pake teknologi ini diperlukan parabola
 (ya iya laaa), 1 parabola alias satellite dish bisa untuk upload ato download…upload nya sekitar 1/10 nya download
(ya iya laaa), 1 parabola alias satellite dish bisa untuk upload ato download…upload nya sekitar 1/10 nya download - WiMax: Wordwide Interoperability for Microwave Access, teknologi terbaru nih…denger2 waktu aceh tsunami, akses teknologi nya pake ini nih…IEEE nyebut ini dengan kode 802.16, yang pasti sih WiMAX operates in a similar way to WiFi, but at higher speeds, over greater distances, and for a greater number of users. It uses a network of WiMAX towers that are similar to cell phone towers. To access a WiMAX network, subscribers must subscribe to an ISP with a WiMAX tower within 10 miles of their location. They also need a WiMAX-enabled computer and a special encryption code to get access to the base station.
VPN singkatan dari Virtual Private Network, A VPN is an encrypted connection between private networks over a public network such as the Internet. Instead of using a dedicated Layer 2 connection such as a leased line, a VPN uses virtual connections called VPN tunnels, which are routed through the Internet from the private network of the company to the remote site or employee host. To address security concerns, broadband services (ISP) provide capabilities for using Virtual Private Network (VPN) connections to a VPN server, which is typically located at the corporate site.
VPN Benefits:
- HEMAT, teknologi VPN memungkinkan organisasi untuk menggunakan internet secara global dan terkoneksi ke remote offices atau remote user ke main corporate site, thus eliminating expensive dedicated WAN links and modem banks.
- Keamanan/Security, VPNs provide the highest level of security by using advanced encryption and authentication protocols that protect data from unauthorized access.
- Scalability, Because VPNs use the Internet infrastructure within ISPs and devices, it is easy to add new users. Corporations are able to add large amounts of capacity without adding significant infrastructure.
- Compatibility, VPN technology is supported by broadband service providers such as DSL and cable, so mobile workers and telecommuters can take advantage of their home high-speed Internet service to access their corporate networks. Business-grade, high-speed broadband connections can also provide a cost-effective solution for connecting remote offices.
-
Site-to-Site VPN

Diliat dari gambar diatas, Site-to-Site VPN konek dari satu network ke network yang lain (contoh HQ ke Branch atau sebaliknya). Each site is equipped with a VPN gateway, such as a router, firewall, VPN concentrator, or security appliance. -
Remote-Site VPN

Remote-access VPNs enable individual hosts, such as telecommuters, mobile users, and extranet consumers, to access a company network securely over the Internet. Each host typically has VPN client software loaded or uses a web-based client. (biasanya ada software VPN buat client konek ke Office atau lewat web-based client)

Singkat kata….Metro Ethernet itu istilah Ethernet yang dipakai “melampaui batas”… By extending Ethernet to the metropolitan area, companies can provide their remote offices with reliable access to applications and data on the corporate headquarters LAN. IP-aware Ethernet switches (switch layer 3 / multi-layer switch) enable service providers to offer enterprises converged voice, data, and video services such as IP telephony, video streaming, imaging, and data storage.
Benefits of Metro Ethernet include:
- Reduced expenses and administration-Metro Ethernet provides a switched, high-bandwidth Layer 2 network capable of managing data, voice, and video all on the same infrastructure. This characteristic increases bandwidth and eliminates expensive conversions to ATM and Frame Relay. The technology enables businesses to inexpensively connect numerous sites in a metropolitan area to each other and to the Internet.
- Easy integration with existing networks-Metro Ethernet connects easily to existing Ethernet LANs, reducing installation costs and time.
- Enhanced business productivity-Metro Ethernet enables businesses to take advantage of productivity-enhancing IP applications that are difficult to implement on TDM or Frame Relay networks, such as hosted IP communications, VoIP, and streaming and broadcast video.
Choosing Connectivity
-
Untuk tujuan apa?Do you want to connect local branches in the same city area, connect remote branches, connect to a single branch, connect to customers, connect to business partners, or some combination of these? If the WAN is for providing authorized customers or business partners limited access to the company intranet, what is the best option?
-
Ruang Lingkup Geografis / Didaerah mana?Is it local, regional, global, one-to-one (single branch), one-to-many branches, many-to-many (distributed)? Depending on the range, some WAN connection options may be better than others.
-
Kebutuhan Traffic-nya seperti apa ?Contoh: if you want to transfer video…the ATM technologies seems to be the best choice, for speed…maybe fiber opfic suit the requirement
-
Private or Public Network ?
- Private: dedicated or not?
- Public: tipe VPN kek apa yang mau di bikin?
-
COST !!Pasti lah….







0 comments:
Post a Comment